Throughout history, several great civilizations have risen to prominence only to eventually experience decline and fall. This article explores 10 of the greatest civilizations that have ever existed and how they crumbled. From the grandeur of empires that once stretched across continents to the brilliance of cultures that illuminated the world with their knowledge, these great civilizations have left an undeniable mark on our collective memory. However, their stories are not merely accounts of ascension but also cautionary tales of decline and collapse. From the Roman Empire’s majestic reach to the mysterious allure of the Mayans, we journey through time to understand the intricacies that shaped their destinies and discover the timeless lessons they bestow upon us.
The List of the 10 of the Greatest Fallen Civilizations
1. The Roman Empire
625 BCE – 476 CE
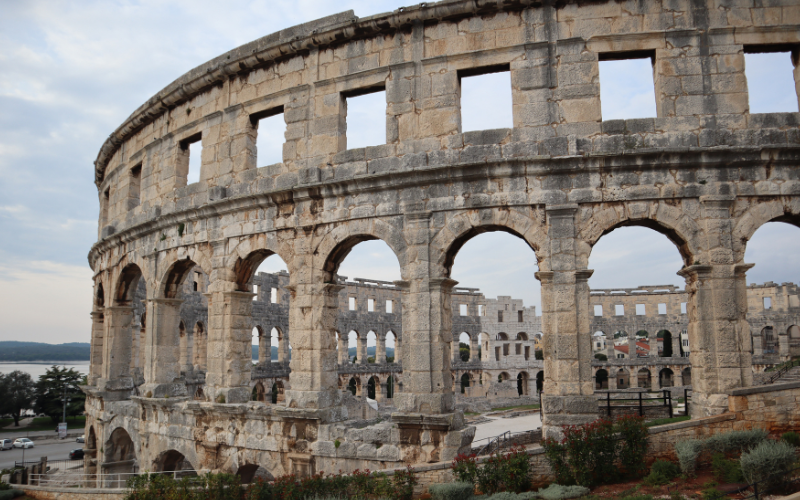

The Western Roman Empire stands as one the greatest civilizations in history, known for its extensive territorial conquests and profound cultural contributions. Yet, this once-mighty civilization would eventually face a decline, characterized by a number of challenges.
An economic downturn would rock its foundations, destroying the financial stability that had fueled its growth. Simultaneously, constant military pressures from external forces strained its defenses, leaving it vulnerable and exposed. However, perhaps the most impactful cracks emerged within its own walls, as internal divisions and political strife would further weaken the empire’s strength.
The year 476 CE would mark Rome’s turning point, as the empire would disintegrate and, with it, the end of ancient Rome’s dominance over Europe. The legacy of the Roman Empire serves as a cautionary tale, a reminder that even the mightiest of civilizations are not immune to the perils of complexity, internal strife, and external pressures.
2. The Byzantine Empire
330 CE – 1453 CE
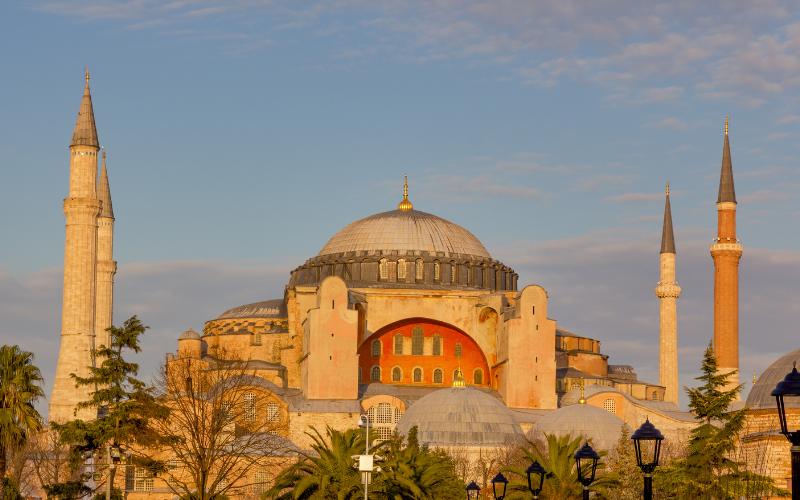

The Byzantine Empire, an enduring institution of the Eastern Roman heritage, would constantly face challenges that would ultimately shape its destiny. This empire, characterized by its distinct fusion of Roman traditions and Greek influences, confronted relentless external pressures.
Drawn by the empire’s wealth and strategic importance, there were constant invasions by an array of groups. Territorial fights were just the tip of the iceberg, as financial strains began to chip away at the empire’s economy, straining its ability to project power. Amidst these issues, the empire would also suffer from internal divisions and religious conflicts between Orthodox Christianity and other faiths.
As centuries passed, the Byzantine Empire faced its defining moment in 1453, when the walls of Constantinople would crumble at the hands of the Ottoman Turks. This marked the end of a millennium of Byzantine rule.
3. The Mayan Civilization
2000 BCE – 16th Century CE
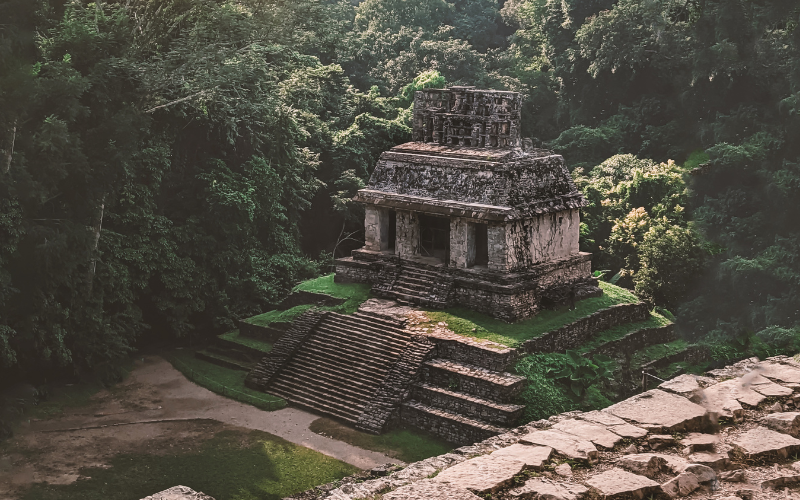

The Mayan Civilization was a mysterious jewel of Mesoamerica. Characterized by its intricate architecture, mathematical achievements, and sophisticated calendar systems, the Mayan people crafted a legacy of intellectualism and cultural refinement.
However, over time, a complex and mysterious decline would ensue. Environmental degradation would occur as a result of unsustainable practices and the strain of supporting a growing population; once fertile lands were being destroyed out of the necessity to support its people.
With that, political instability would follow, as power dynamics shifted and internal conflicts would follow. The once sophisticated trade routes would undergo a drastic transformation destroying their ability to prosper. Over time, these threads of adversity would intertwine and gradually unravel the civilization.
Read More Fun Facts
Learn more fun facts with Trivia Mastermind content.
4. The Mongol Empire
1206 CE – 1368 CE
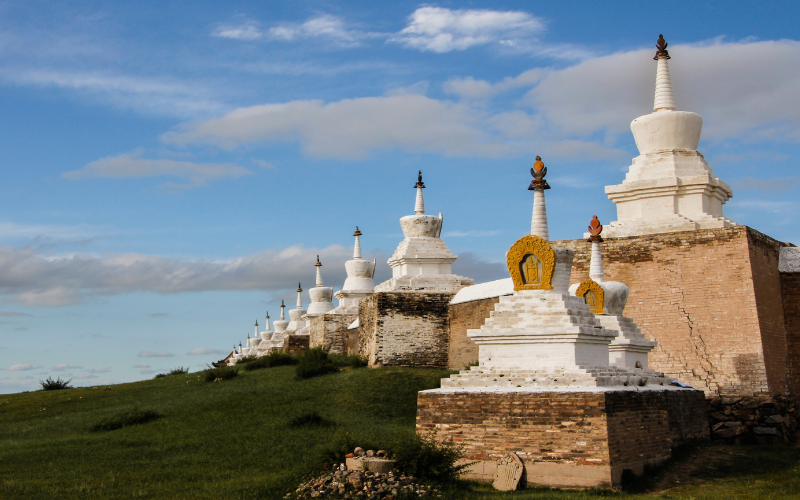

The Mongolian Empire was once an unparalleled force of conquest and expansion. It would emerge under the visionary leadership of Genghis Khan and his successors. The empire’s influence stretched from Mongolia to the edges of civilization. To this day, Genghis Khan’s strategic brilliance and his military might remain unmatched.
However, as the empire would constantly expand, it fostered the challenges of governance on an unprecedented scale. Internal conflicts would inevitably occur, as ambitious leaders vied for power, hurting the unity that had once fueled their conquests.
The intricate web of alliances and loyalties woven across the territories they had conquered would become increasingly difficult to maintain. As the empire’s enormous size would lead to its fragmentation. The once-unstoppable momentum gradually gave way to the complexities of internal and external pressures.
5. The Ancient Egyptian Civilization
3150 BCE – 30 BCE
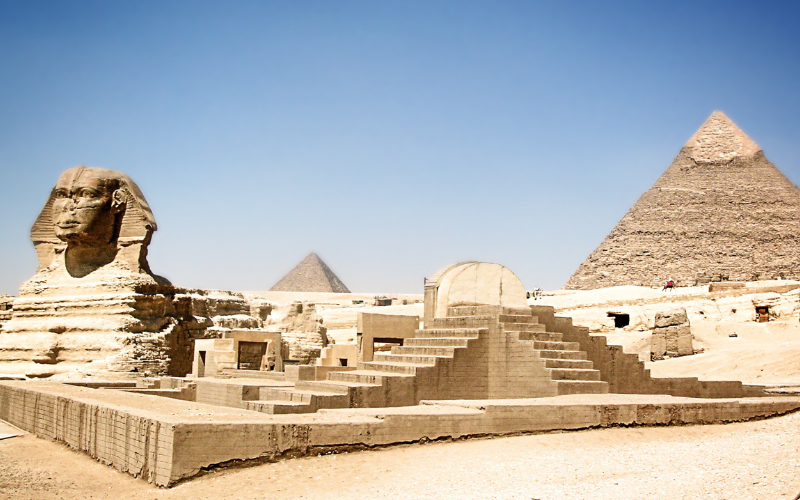

The history of Ancient Egypt demonstrates remnants of grandeur, with much left to be a mystery. From the colossal pyramids of the desert, to the intricate hieroglyphs etched on temple walls, Egypt’s legacy continues to endure.
As time passed, the once-unified society found itself shaken by political complexity. The transition from powerful pharaohs to periods of fragmented rule eroded the foundation of stability. The balance between central authority and governors gradually eroded, leading to internal conflict. With that, the lack of a strong, unifying force exposed Egypt’s vulnerability to external threats.
Eventually, Egypt would have to deal with formidable empires beyond its borders. Alexander the Great would bring Hellenistic influences that blended with Egypt’s ancient traditions, altering its identity. As time passed, Egypt would find itself bound to the Roman Empire. Rome’s legions would bear down on the banks of the Nile, and Egypt’s society would shift again. The fall of Alexandria, a city renowned for its grandeur and scholarship, marked a major turning point where it would lose its autonomy.
6. The Ottoman Empire
1299 CE – 1922 CE
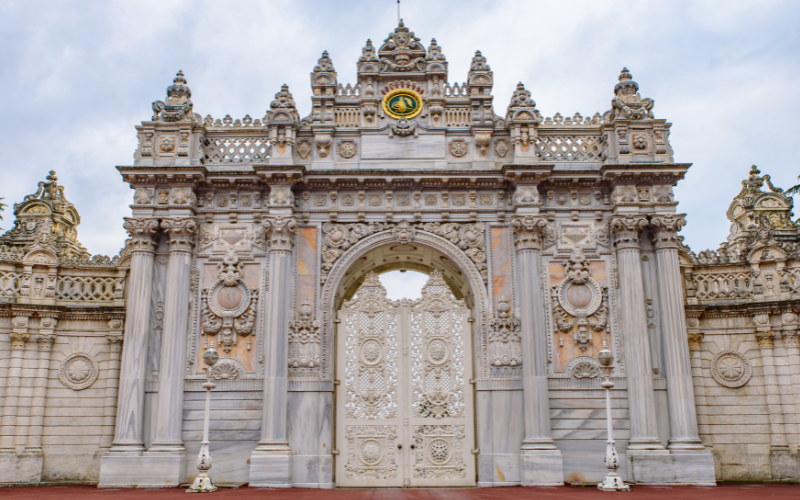

The Ottoman Empire had a colossal history spanning centuries. From its birth in Anatolia, this empire spread its rule across massive territories, embracing diverse cultures and leaving an undeniable mark on the world. As the empire grew, the influence from a diversity of cultures from East and West became apparent. Its architecture, art, and contributions to science left an enduring legacy that still resonates in the modern world.
Unfortunately as with many great empires, internal strife and rivalries were growing out of the desire for more power from factions. As sultans passed, there would be inevitable periods of instability that strained the empire’s unity. The empire’s once-thriving economy began to show signs of strain. Trade routes that had once dominated, faced new rivals and pathways, affecting economic sustainability.
With the rise of European powers, the Ottoman Empire would face these emerging forces, resulting in territorial losses and waning influence. The culmination of this played out on the stage of World War I, with the empire standing on the losing side of the global conflict, and its dissolution inevitable.
Play Trivia!
Challenge yourself and play trivia questions with answers and explanations.
7. The Inca Empire
1438 CE – 1533 CE
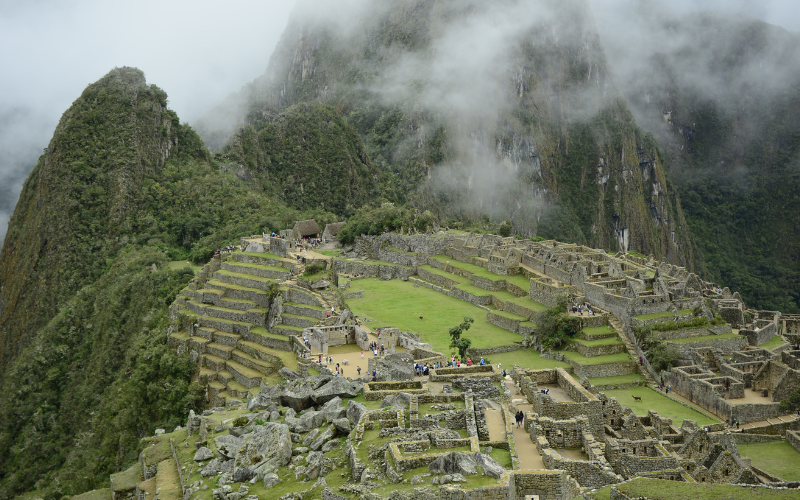

The Inca Empire is known throughout history for its impressive architecture, sophisticated road systems, and ingenious agricultural practices. For a time, they stood out as the pinnacle of historical human innovation.
The Inca Empire was also known as Tawantinsuyu. Its domain stretched across a vast landscape, from the coastal deserts to the peaks of the Andes. Elaborate stone architecture filled their cities, with Machu Picchu serving as an iconic testament to their engineering capability.
However, as the empire flourished, the arrival of Francisco Pizarro and Spanish conquistadors would lead to devastating changes. With advanced weaponry and inadvertently, devastating diseases, its population and society were destroyed.
The Inca initially attempted diplomacy, but their efforts were met with betrayal, as Pizarro would capture the Inca emperor Atahualpa, leading to the eventual downfall of the empire. The Spanish exploited internal divisions, using local allies and superior weaponry to overpower the Inca. In just a few short years, the empire that had stood for centuries crumbled under the weight of conquest. The Inca’s cultural heritage would also suffer a devastating blow as the Spanish dismantled temples, looted treasures, and suppressed their traditions.
8. The Aztec Empire
1300 CE – 1521 CE
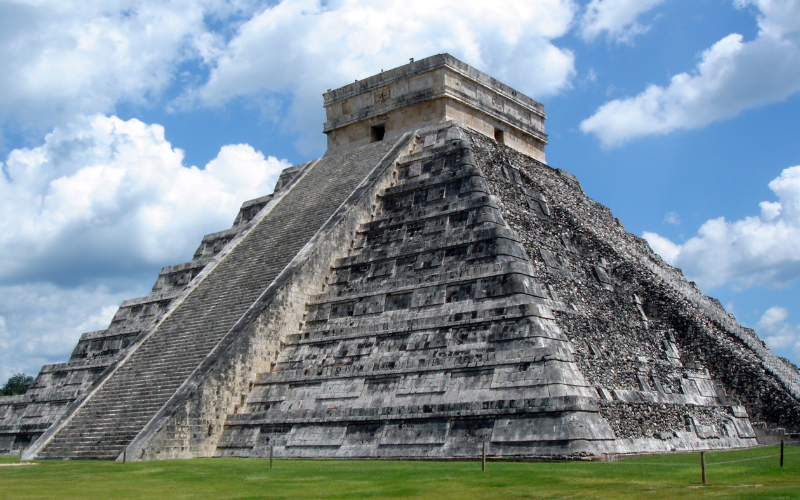

In the heart of Mesoamerica, the Aztec Empire emerged as a formidable force. The Empire existed in present-day Mexico, with its grand pyramids, intricate artistry, and sophisticated societal structure. The Aztecs were also known as the Mexica. They had established their capital, Tenochtitlan, on the site of modern-day Mexico City. A society with a hierarchical structure, the Aztecs practiced advanced agriculture, built intricate causeways, and maintained a complex calendar system that reflected their connection to the cosmos.
Yet, the Aztecs would be met by formidable external forces. In 1519, Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés and his men arrived on the shores of Mexico, leading to a clash of civilizations. Cortés exploited internal divisions among different indigenous groups, leveraging their resentments toward the Aztecs.
The Aztecs initially mistook the Spanish for gods due to their unfamiliar appearance and advanced weaponry. The Spaniards took advantage of this by stoking internal strife, forging alliances with local indigenous groups, and joining forces against the Aztecs. Moreover, the Aztec Empire would face new foreign diseases brought over by the visitors, destroying the Aztec population and altering the balance of power. In 1521, after a brutal siege, Tenochtitlan fell to the Spanish forces. The city, once a symbol of Aztec grandeur, was reduced to ruins.
9. The Hittite Empire
1600 BCE -1200 BCE
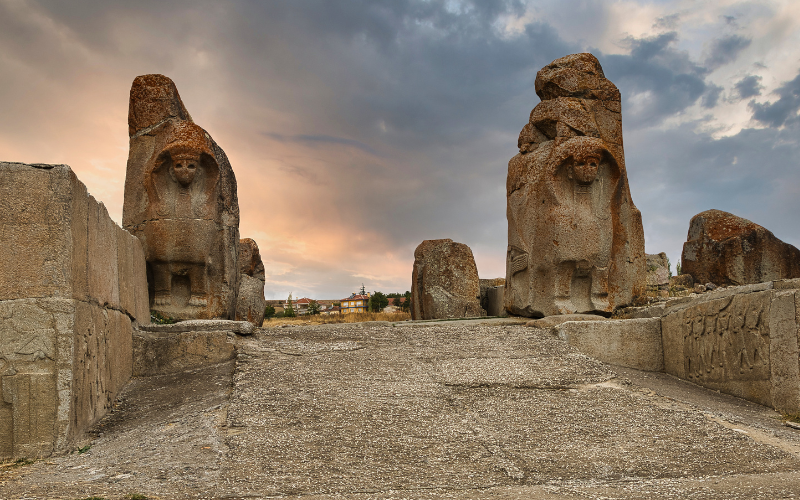

In the heart of Anatolia, the Hittite Empire emerged as a dominant force that shaped the landscape of the ancient Near East. The Hittite Empire reached its peak during the Late Bronze Age, with an advanced military, impressive architecture, and a sophisticated legal code.
Their capital city, Hattusa, stood as a testament to their architectural capability. However, as the empire flourished, it also faced challenges that would eventually contribute to its decline. The Hittite heartland was surrounded by formidable adversaries, including the powerful Egyptian New Kingdom, the Assyrians, and the Mycenaeans. These neighboring powers sought to expand their territories through conquest.
Internal conflicts and succession struggles would also lead to the Hittite Empire’s decline. The death of a strong leadership would drive rival factions to vie for power and lead to more instability. Economic pressures and changing trade routes would also add strain to the empire’s resources and ability to maintain its hold over its huge territories.
Around 1200 BCE, a tumultuous period would ensue where waves of invasions and migrations swept across the region, forever altering the geopolitical landscape, including the decline of the Hittite Empire.
10. The Sumerian Civilization
4100 BCE – 1750 BCE
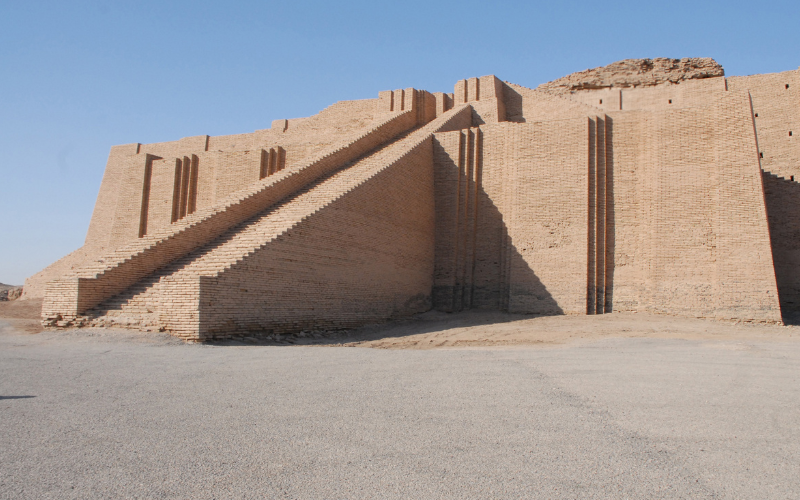

The Sumerians of ancient Mesopotamia carved their legacy as pioneers of urbanization, governance, and cultural advancement. With fertile lands between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, a complex society, marked by monumental architecture, intricate writing systems, and organized governance would magnificently exist.
The Sumerian civilization flourished at its height, with a number of city-states, rulers, religious practices, and distinct identities. However, the path of Sumer would eventually face factors leading to its decline. Once fertile lands began to face challenges, straining resources and destabilizing the advanced Sumerian society.
The Sumerians would also face external pressures from neighboring groups. The Akkadian Empire, led by Sargon the Great, would conquer the Sumerians, bringing political change, cultural amalgamation, and power shifts.
Shifts in trade routes also played a role in Sumer’s decline. The prosperity of Sumer was intricately linked to its position as a trading hub, facilitating the exchange of goods across the ancient world. As trade routes shifted and new avenues of commerce opened, Sumer’s economic influence waned, impacting its economic stability and geopolitical significance.
Conclusion
As we reflect on the fates of these 10 once-mighty civilizations, we realize the lessons that should be taken from their failures. The rise and fall of civilizations, though shaped by unique circumstances, bear common threads of human nature, governance, environment, and societal dynamics. These narratives serve as a reminder that even the grandest empires are not impervious to pitfalls. From the Roman Empire’s internal strife to the Maya civilization’s environmental challenges, and from the Byzantine Empire’s religious conflicts to the Aztec Empire’s encounter with foreign conquerors, these stories paint a vivid portrait of the intricate web of factors that can contribute to a civilization’s collapse. By embracing the wisdom embedded in these fallen legacies, we gain insights that are relevant for societies today and tomorrow, hopefully to illuminate our path forward.
Read More Fun Facts
Learn more fun facts with Trivia Mastermind content.
Play Trivia!
Challenge yourself and play trivia questions with answers and explanations.
Recent Posts
Step into a realm of nostalgia as we embark on a journey through the annals of pop culture and bid farewell to 35 recently obsolete technologies. In the ever-evolving landscape of innovation, certain...